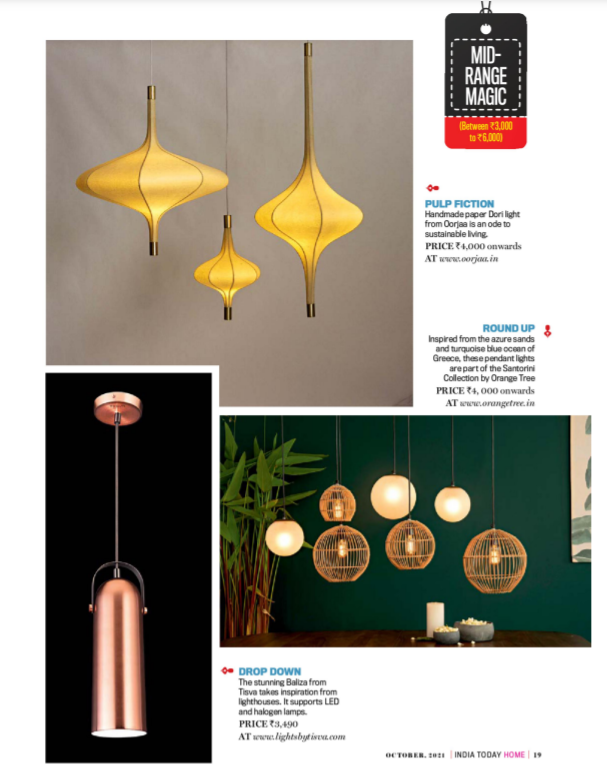
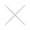
Psychology of Light
Emotional Impact It is easy to simply light up a place with general light; however with all areas equally lit, the space will lose out on its emotional value. Moreover it will create a dull and boring place, where people will tend to get depressed. It requires careful manipulation of light to create spaces that […]